Latest bulletins in quantum computing have introduced renewed consideration to the query of how these advances may affect Bitcoin. In a newly revealed report, we offer an outline of the present state of quantum computing, the risk mannequin for Bitcoin, and the subsequent steps being thought-about. This publish gives a abstract of our key findings and suggestions. See the total report right here.
Timeline for Bitcoin Preparation to Quantum Computing
We define a dual-track migration technique for Bitcoin in response to the potential emergence of quantum computing.
Lengthy-Time period Path: This complete strategy assumes that there’s nonetheless a considerable window of time earlier than quantum computing poses a sensible risk. Drawing on the timelines of prior protocol upgrades similar to SegWit and Taproot, we estimate that implementing a full quantum-safe transition may take roughly 7 years.
Quick-Time period Contingency Path: This monitor serves as an emergency response within the occasion of a sudden breakthrough in quantum computing. It prioritizes a fast deployment of protecting measures to safe the Bitcoin community and could possibly be executed in roughly 2 years.
In each eventualities, funds which are fastidiously managed, i.e., saved in hashed deal with varieties like P2PKH or P2WPKH with out deal with reuse, are already shielded from quantum assaults. Nevertheless, spending these funds in a post-quantum safe manner would require extra infrastructure, which is anticipated to be developed through the second part of both timeline
Quantum Computer systems: When Are They Coming, and What Will They Be Succesful Of?
If realized at scale, quantum computing may supply important speed-ups for particular courses of issues by harnessing the ideas of quantum mechanics. Of explicit concern are cryptographically related quantum computer systems (CRQCs), machines able to breaking the mathematical assumptions underlying fashionable cryptography. This consists of algorithms like Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), which is prime to Bitcoin’s safety.
Whereas quantum computing has been an energetic space of theoretical analysis for many years, important engineering challenges stay in constructing large-scale quantum machines, particularly CRQCs. To this point, no quantum pc has surpassed classical supercomputers in fixing commercially related issues, nor demonstrated the capabilities wanted to threaten fashionable cryptography.
Estimated timelines for CRQCs
Technological progress is notoriously exhausting to foretell, it hardly ever follows a linear path, and historical past gives many examples of sudden breakthroughs. In anticipation of potential shifts within the cryptographic panorama, a number of organizations have proposed timelines for transitioning cryptographic signatures.
Some of the distinguished efforts comes from the U.S. Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise (NIST), which has been main the event of cryptographic requirements. Their revealed suggestions spotlight two key dates:
By 2030, conventional encryption strategies, similar to ECDSA and RSA, must be phased out.
By 2035, all cryptographic techniques ought to transition absolutely to post-quantum algorithms.
The UK’s Nationwide Cyber Safety Centre follows a comparable strategy with a three-phase migration framework that goals to finish the transition to post-quantum cryptography by 2035. Different entities, such because the EU and China, are additionally actively engaged on post-quantum cryptography methods, although they haven’t but revealed formal timelines.
On the trade stage, a number of main firms, together with Cloudflare, Sign, and Google, have begun adopting post-quantum cryptography. They’re implementing hybrid signature schemes that mix conventional encryption strategies with post-quantum algorithms, requiring an attacker to interrupt each so as to compromise the system. Apple has additionally introduced plans to transition to post-quantum cryptography. As PQC turns into an rising trade normal, extra firms are anticipated to comply with go well with.
What’s at Stake?
The monetary stakes of the risk to Bitcoin are substantial. Fig 2 illustrates evaluation revealing that roughly ~6.51 million bitcoin, value over $700 billion at present valuations, and representing 32.7% of present provide, is quantum susceptible. This consists of funds held in addresses which have practiced deal with reuse, funds secured by inherently quantum-vulnerable script varieties, and funds which are susceptible through public key publicity on forks of Bitcoin, similar to Bitcoin Money.
Bitcoin Menace Mannequin: What Ought to We Be Nervous About?
Quantum computing is anticipated to affect two key areas of Bitcoin: mining and transaction signatures. In quantum mining, the problem of mixing the facility of a number of machines offers a disproportionate benefit to massive quantum miners, threatening decentralization. For transaction signatures, the chance is extra direct, a CRQC may derive non-public keys from public keys, enabling theft of funds.
Importantly, the timelines for these two threats differ considerably. Constructing a quantum pc that may outperform fashionable ASIC miners presents a far higher engineering problem than setting up one able to breaking digital signatures. That is due, partially, to the low clock speeds of quantum processors, that are a lot slower than the extremely optimized and specialised {hardware} utilized in Bitcoin mining and the dearth of parallelization.
Signatures
A CRQC may break the idea that it’s infeasible to derive a non-public key from its corresponding public key underneath ECC primarily based schemes, doubtlessly permitting attackers to steal funds. In Bitcoin, possession of a UTXO is confirmed by signing a transaction with the non-public key equivalent to a given public key. If a CRQC can derive that personal key from the general public key, it may possibly falsely declare possession and spend the funds.
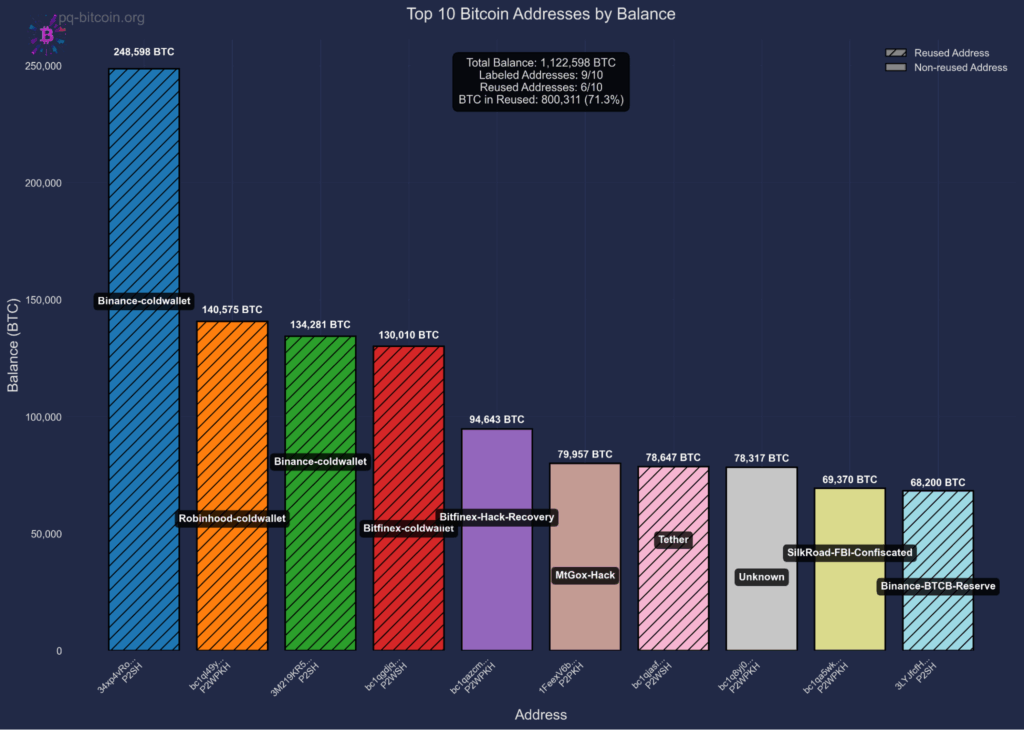
This results in two distinct quantum assault eventualities. When spending from hashed addresses, public keys are revealed briefly, giving attackers a short window, sometimes minutes to hours, to derive non-public keys and steal funds, probably by way of chain reorganization. In distinction, sure output varieties (P2PK, P2MS, P2TR) expose public keys completely on-chain from the second funds are acquired, giving attackers limitless time to mount quantum assaults. Handle reuse converts the short-term vulnerability of hashed addresses into everlasting publicity, as public keys stay seen on-chain after the primary spend. As proven in Fig 3, probably the most susceptible targets are addresses that maintain important funds with uncovered public keys similar to institutional holdings that practiced deal with reuse.
Mining
Bitcoin mining is predicated on the precept that the chance of discovering a legitimate block scales linearly with the quantity of computational effort expended. Grover’s algorithm, a quantum search method, gives a quadratic speedup for brute-force search. Nevertheless, not like classical mining, Grover’s algorithm just isn’t simply parallelizable. This limitation may give a disproportionate benefit to entities with entry to large-scale, centralized quantum {hardware}, doubtlessly growing mining centralization moderately than broadening participation.
Along with issues about centralization, quantum mining may alter miners’ optimum methods, doubtlessly degrading chain high quality, for instance, by growing the speed of stale blocks. A better stale block fee could make sure assaults (similar to egocentric mining or double-spends) less expensive and extra possible.
As famous earlier, constructing a quantum pc able to outperforming fashionable ASIC miners is believed to be a lot farther off than growing CRQCs. As such, quantum mining just isn’t a direct concern and is unlikely to be a sensible risk within the coming many years. Nonetheless, exploring Proof-of-Work mechanisms in a future quantum context stays a worthwhile analysis path. Creating a greater understanding of the potential dangers and mitigation methods would assist the ecosystem put together for a world the place quantum mining turns into possible.
Migration to Quantum Safety: What are the primary challenges?
Quantum-Safe Signatures
Quantum-secure cryptographic signatures have been studied for many years, however curiosity and progress have accelerated lately. This has led to the event of candidate protocols similar to SPHINCS+, FALCON, and others. Nevertheless, as a comparatively younger discipline, it has seen a number of proposed schemes initially believed to be safe however have been later damaged (e.g. SIKE), even by classical computer systems. Whereas belief within the present candidates is rising over time, the sphere stays energetic and evolving.
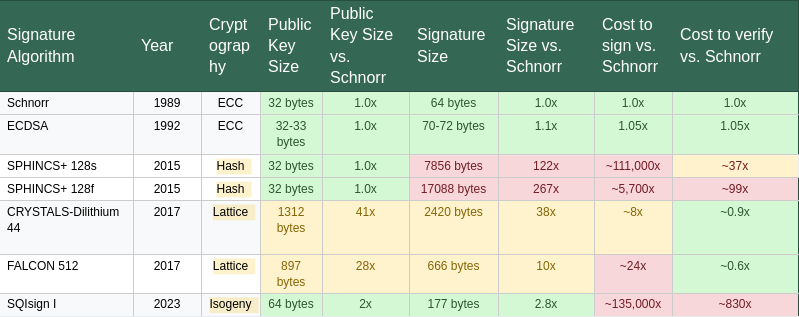
As detailed in Desk 1, a major limitation of post-quantum signature schemes is their considerably bigger key and signature sizes, together with elevated verification instances, relative to classical algorithms similar to ECDSA and Schnorr which are at present utilized in Bitcoin. To handle this, some proposals counsel leveraging SegWit’s witness low cost mechanism to cut back on-chain footprint. Nevertheless, one of the best strategy for integrating quantum-secure signatures into the protocol stays an open query. Along with efficiency trade-offs, quantum-secure schemes don’t but help the total vary of performance supplied by classical signatures, similar to these relied upon within the Lightning Community and different functions. This space continues to be an energetic focus of analysis throughout the cryptography neighborhood, and additional enhancements are anticipated within the coming years.
Migration Pathways
If the Bitcoin neighborhood chooses emigrate susceptible funds to quantum-resistant codecs, numerous UTXOs will must be moved. A number of approaches are into account, every making completely different tradeoffs. Some concentrate on enabling safe spending of hashed-address outputs with out exposing the general public key prematurely. Others suggest mechanisms to restrict or regulate the spending of UTXOs which are straight susceptible to quantum theft. These methods typically require modifications to consensus guidelines, similar to gentle forks, and should additionally account for the sensible problem of transferring a big quantity of UTXOs, doubtlessly taking 4 to 18 months even with sustained allocation of block area.
Philosophical Dilemma: Will we permit funds to be stolen?
The Bitcoin neighborhood faces a basic philosophical query: ought to quantum-vulnerable funds be made completely unspendable (“burned”) or stay accessible to quantum computer systems (“stolen”)? This resolution touches Bitcoin’s core ideas of property rights, censorship resistance, and immutability. The burn strategy treats quantum vulnerability as a protocol bug requiring a conservative repair, stopping wealth redistribution to those that win the CRQC race. The steal strategy maintains that burning funds violates the property rights of their homeowners, successfully confiscating property from those that might merely be unaware of the risk or unable emigrate in time.
The implications lengthen past philosophy to market dynamics. A coordinated burn would completely take away thousands and thousands of bitcoins from circulation, doubtlessly growing the worth of remaining cash whereas offering market certainty. Permitting quantum theft permits large wealth switch to entities with quantum capabilities, doubtlessly creating extended market uncertainty and volatility as funds are progressively drained. A call on this matter is a defining second for Bitcoin’s governance mannequin, requiring the neighborhood to stability safety imperatives towards foundational ideas of person sovereignty and non-intervention.
So, what’s subsequent?
The arrival of CRQCs would mark a significant shift throughout the digital panorama, putting a lot of right this moment’s safe communication, authentication, and digital infrastructure in danger. Whereas quantum computing just isn’t but a sensible actuality, preparations are underway to assist guarantee Bitcoin’s resilience towards future developments. Analysis continues throughout each the cryptographic and Bitcoin communities to evaluate potential dangers and discover sensible responses. Our report highlights two areas that will warrant near-term consideration: stopping deal with reuse and evaluating the trade-offs within the Burn vs. Steal dialogue round uncovered funds.
The window for proactive motion is open now, although it might not stay open indefinitely. Staying knowledgeable about advances in quantum computing and cryptography is important, as is learning potential mitigation methods and their broader implications for the Bitcoin ecosystem. Guaranteeing Bitcoin’s long-term safety in a post-quantum world requires considerate, deliberate work, beginning now, so we will make well-informed choices whereas time continues to be on our facet.
It is a visitor publish by Clara Shikhelman and Anthony Milton. Opinions expressed are solely their very own and don’t essentially mirror these of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Journal.









